The thyroid is responsible for producing hormones that control certain functions, including your metabolism and heart rate. There are a number of diseases that can affect this gland, ranging from an over- or under-production of thyroid hormones to cancer.
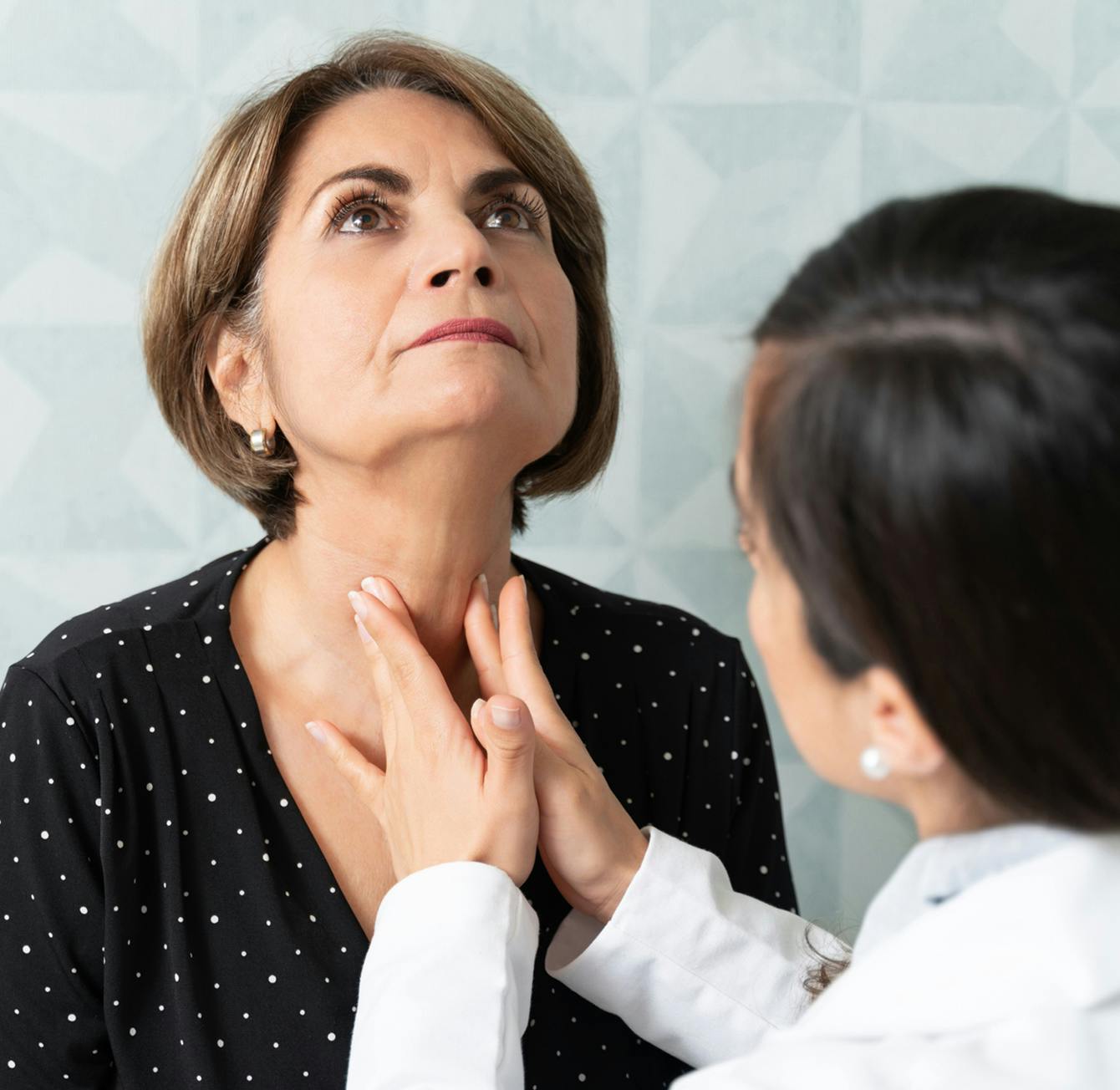
How is Thyroid Disease Diagnosed?
Thyroid disease can be diagnosed during a visit to your ENT. During that appointment, your doctor will begin by feeling your neck to look for lumps, enlarged areas and irregularities relating to your thyroid. From there, blood tests may be ordered to assess the function of the gland and the amount of certain hormones present in your blood. Depending on these findings, additional imaging tests, such as a CT scan, MRI or ultrasound, may be ordered to obtain a definitive diagnosis. If a suspicious thyroid lump or nodule is found, a biopsy may be performed. This involves inserting a thin needle directly into the lump and extracting cells to evaluate for cancer.


